High-Availability Deployment
PrivX high availability (HA) deployment is supported in both on-premises and cloud environments. For AWS-based deployments, see CDK-based installation scripts at https://github.com/SSHcom/privx-on-aws.
Load Balancer
For high-availability (HA) installations, PrivX must run behind a load balancer. We recommend using an HTTPS load balancer that terminates TLS certificates and forwards traffic to PrivX Server instances. Direct access to PrivX Server instances should be blocked. This way, This ensures that only the load balancer requires a valid TLS certificate, simplifying certificate management.
When deploying PrivX components (Extender, Carrier, Web Proxy) in an HA setup, an HTTPS load balancer with sticky sessions (affinity cookies) is required.
Supported and Tested Load Balancers
AWS, Azure, and Google load balancers have been officially tested, and PrivX components are preconfigured to work with AWS, Azure, Google, Kubernetes Ingress, and Nginx Plus . Other load balancers might require additional settings.
For on-premises environments, most HTTPS load balancers (e.g., HAProxy, Nginx Plus, NetScaler) are supported, as long as they provide sticky sessions and preferably active health checks.
Load Balancing Algorithms
For Extender, Carrier, and Web Proxy, use a Round-Robin routing algorithm (not least connections). However, if these components are not used any load balancing algorithm or network load balancer is acceptable.
Native Client Traffic
For native SSH Bastion and native RDP client traffic, a TCP load balancer or DNS load balancing is required. You may also use two load balancers for the same PrivX servers: one HTTPS load balancer for the web UI and PrivX components, and one TLS network load balancer for native client traffic.
If the optional client certificate authentication is enabled for the web UI, a TLS load balancer must be used.
Health Checks and Autoscaling
We recommend using the monitor-service instance status endpoint for health checks to check PrivX instance availability:
https://<privx_lb_endpoint>/monitor-service/api/v1/instance/status
Alternatively, other microservice status endpoints may be used:
https://<privx_lb_endpoint>/<servicename>/api/v1/status
However, using the active health checks at the monitor-service endpoint is recommended, as it avoids unexpected service downtime.
Load Balancing PrivX Components
For load balancing PrivX components, both Extender and web components (Carrier and Web Proxy) can be grouped using Routing Prefix settings in the PrivX UI. For example, setting the same Routing Prefix variable for two or more different Extenders will group them logically, allowing PrivX to load balance between them. This feature still requires separate configuration files for each component. Sharing configuration files or credentials between components is not currently supported.
Load balancing algorithms (least connections or round-robin) can be changed in the PrivX configuration.
Standard HA installation
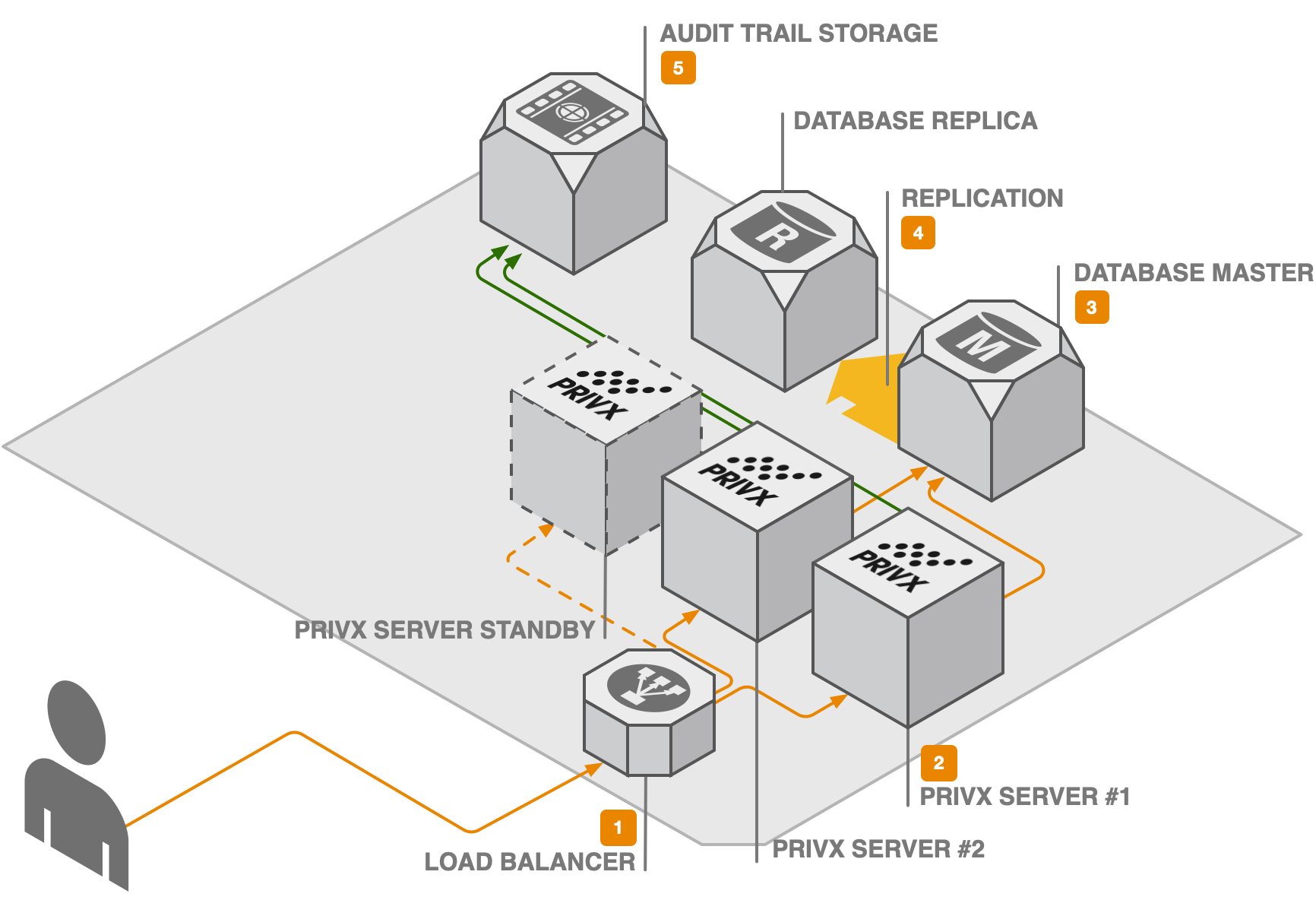
-
A load balancer directs traffic to a specific PrivX application server. The load balancer keeps track of PrivX application server statuses and removes non-working ones from the pool. The load balancing can be based on either source address or sticky session.
info- Sticky session (session affinity cookie) configuration for the load balancer is recommended.
- Sticky load balancer cookies with round-robin routing algorithm are required if using PrivX Extender, Carrier and Web Proxy components with more than one PrivX node.
-
Each PrivX application server consists of an Nginx reverse proxy and many PrivX microservices. The microservices offer REST APIs over HTTPS to the clients, and the reverse proxy serves PrivX HTML5 UI static resources.
Once a PrivX application server has been configured, new application nodes can be added by simply taking a snapshop of the original node and deploying it for new instances.
-
The PrivX microservices persist data to a PostgreSQL database.
-
PostgreSQL databases should also be highly available (master-slave mode or cluster), thus, having replicas. The database should be set to clustered mode. This way, if the master database dies, pre-configured DNS failover PrivX servers can contact replicas via configuration or DNS changes.
PrivX also supports various Hardware Security Modules (optional) for storing keys.
-
The trail storage (by default at
/var/privx/audit) receives audit events from the PrivX instances, and it should be mounted on NFS or a secure NAS device -- shared between instances. To avoid file permission issues, ensure that the sameprivxuser and group ID is used in all PrivX application servers.
On-premises PrivX Server HA Setup
The high-level steps for setting up PrivX in HA configuration involves:
- Setting up one initial PrivX node.
- Setting up additional PrivX servers by duplicating the initial PrivX node.
These HA installation instructions apply to non-cloud environment. The HA setup is more recommended for on-premises environments. However, for cloud HA deployment, see Deploying PrivX to Amazon Web Services.
Initial PrivX Node Setup
-
Install PostgreSQL master and slave nodes and configure a replication model that best suits your environment (vendor instructions at https://www.postgresql.org/docs/16/different-replication-solutions.html)
-
Install PrivX from the PrivX repository or from the RPM package:
# From the repository
sudo yum install PrivX# From the RPM package
sudo yum install PrivX-*.x86_64.rpm -
Run the
postinstallconfiguration script with:sudo /opt/privx/scripts/postinstall.shDuring
postinstall.shexecution, instruct PrivX to connect to the external database. -
Verify that the installation works by connecting to the initial PrivX node via browser.
After completing these steps, the initial PrivX node should be setup and ready.
Additional PrivX Nodes Setup
If using physical servers
Create a backup of the initial PrivX node and use it to create additional nodes.
-
On the initial PrivX node, create a backup by running:
sudo /opt/privx/scripts/backup.shThis saves a backup to
/var/backups/privx/hostname_yyyy-mm-dd-hhmm, replacing hostname, date and time accordingly. -
For each addition node you have, set up PrivX using the backup:
-
Transfer the backup directory to the node.
-
Install PrivX without running postinstall.
If installing from repository:
sudo export SKIP_POSTINSTALL=1
sudo yum install PrivXIf installing from RPM package:
sudo export SKIP_POSTINSTALL=1
sudo yum install PrivX-*.x86_64.rpm -
Duplicate the PrivX setup from the backup by running (replacing the path to the backup as needed):
sudo /opt/privx/scripts/restore.sh /path/to/backup/directory/from/node/one/hostname_yyyy-mm-dd-hhmm` -
Finish the setup by running postinstall:
sudo /opt/privx/scripts/postinstall.sh
-
If Using Virtual Machines
After installing PrivX to the first node, you can clone the node and use the cloned instance to launch additional PrivX nodes.
To ensure that all machines have a unique machine ID, you may need to regenerate it on cloned machines.
Extender HA Setup
Extenders are grouped into HA clusters by Routing prefix. Extenders with equivalent routing prefixes belong in the same HA cluster. When an Extender is down, connections are established via other available Extenders from the same HA cluster.
For a HA Extender setup, you must configure two or more Extenders, and all Extenders in the HA cluster must have the same Routing prefix.
For more information about setting up Extenders, see PrivX Extender Setup.
Carrier and Web Proxy HA Setup
PrivX Carriers and PrivX Web Proxies are grouped into HA clusters by Routing prefix. Pairs of Carrier and Web Proxy that have equivalent routing prefixes belong in the same HA cluster. When a Carrier/Web Proxy pair is down, connections are established via other available Carrier/Web Proxy pairs from the same HA cluster.
For a HA Carrier and Web Proxy setup, you must configure two or more Carrier/Web Proxy pairs, and all Carriers/Web Proxies pairs in the HA cluster must have the same Routing prefix.
For more information, see [PrivX Carrier and Web Proxy Setup](../setting-up-privx-components/#privx-carrier-and-Web Proxy-setup).
Just like Extenders, each Carrier/Web Proxy pair requires its own credentials and configuration file. You will need to manually ensure that all configuration files for the same HA cluster have the same routing prefix.
High Availability Upgrade
These high-availability (HA) upgrade instructions apply to non-cloud environment, but may be adapted to some cloud HA setups as well.
Ensure the PrivX database has enough free space before upgrading, and note that migrations during upgrade may temporarily triple the database size. If necessary, you may reduce the database size before upgrade with Data Retention settings.
We strongly recommend backing up the PrivX database and PrivX server config files before upgrade, to allow restoring the previous version in case of a failed upgrade.
You can upgrade your HA deployment in two ways:
- Zero-Downtime Upgrade: Upgrade while allowing users to log in and connect to hosts. Only allows upgrading to later minor releases or the next major version.
- HA Upgrade with downtime: PrivX will be unavailable during upgrade. Use this to upgrade over multiple major versions at once.
Zero-Downtime Upgrade
The high-level steps for Zero-Downtime Upgrade (ZDU) are:
- Upgrading each PrivX Server.
- Finalizing the upgrade.
ZDU is only supported if your current PrivX version is 32 or later.
ZDU only allows upgrading to the following versions:
- Later minor releases within the same major version (e.g., from 33.0 to 33.2)
- The next major version (e.g., from 32.x to 33.x).
If your current PrivX version is too old, or if you need to upgrade over multiple major versions at once, use HA Upgrade with Downtime instead.
To upgrade PrivX Servers, perform the following on each PrivX Server:
-
If you are upgrading from PrivX 33.x or later, you can skip this step. Otherwise, save the following upgrade script to a file on the PrivX Server and name it
upgrade_first_stage.sh:#!/bin/bash
UPGRADE_STYLE=no_downtime yum install "$@"Ensure that the script can be run as root (replace
path/to/upgrade_first_stage.shaccordingly):sudo chown root:root path/to/upgrade_first_stage.sh
sudo chmod u+x path/to/upgrade_first_stage.shThe rest of this article assumes that the upgrade script is saved at
/opt/privx/scripts/upgrade_first_stage.sh. -
If you are installing from RPM (instead of the PrivX repository), copy the RPM package to the PrivX Server.
-
Run the
/opt/privx/scripts/upgrade_first_stage.shscript to install the new packages.-
If upgrading from PrivX repository (replace
xx.xwith the version you are upgrading to):sudo /opt/privx/scripts/upgrade_first_stage.sh PrivX-xx.x -
If upgrading from RPM (replace
path/to/PrivX.rpmwith the path where you saved the RPM package):sudo /opt/privx/scripts/upgrade_first_stage.sh path/to/PrivX.rpm
This upgrades the current PrivX Server. Therefore, you must repeat these steps on the remaining servers.
-
Once the upgrade on the first PrivX Server is complete, your PrivX deployment will be in maintenance mode, that is, users can log into PrivX and connect to hosts, but other PrivX features are disabled until the ZDU is finalized.
For more information about the features during ZDU, see Features Available During Zero-Downtime Upgrade.
Upgrade disconnects all ongoing connections handled by the current PrivX Server. Users may reconnect immediately via other PrivX Servers while ZDU is in progress.
After all PrivX Servers are upgraded, finalize the upgrade by running the following script once on any PrivX Server:
sudo /opt/privx/scripts/upgrade_second_stage.sh
If performing ZDU from version 32, the upgrade_second_stage.sh script won't be available until after you have run upgrade_first_stage.sh.
Once the script execution is over, the ZDU is complete. Your PrivX deployment should be upgraded, and all PrivX features should be available again.
HA Upgrade with Downtime
-
Choose a PrivX server to upgrade -- any PrivX server in deployment. For these instructions, consider the chosen server as the primary node. Other PrivX servers are called secondary nodes.
-
On all secondary nodes, stop the PrivX service with:
sudo systemctl stop privxThis prevents secondary nodes from writing conflicting data to the database while the primary node is being upgraded.
-
On the primary node, upgrade PrivX:
-
Upgrade PrivX from the repository:
sudo yum install PrivXOr from the RPM package:
sudo yum install PrivX-*.x86_64.rpmThis command upgrades the PrivX database and the PrivX software on the primary node.
-
Verify that the node works before proceeding.
infoOn upgrade, the
postinstall.shscript is run automatically. This also automatically restarts the PrivX services on the node. -
-
On all secondary nodes, upgrade PrivX::
-
If your PrivX servers use individual installation directories (default), upgrade and configure the nodes with
sudo yum install PrivXorsudo yum install PrivX-*.x86_64.rpm. -
If your PrivX servers use a shared NFS-mounted installation directory, you only need to configure the nodes by running
sudo /opt/privx/scripts/postinstall.shon them.
Secondary nodes can be upgraded in parallel.
-